Combatting the Health Risks of ‘The New Smoking’: Prolonged Sitting
Introduction
Prolonged sitting has been labelled as “the new smoking” due to mounting evidence that suggests its harmful on overall health. Whether it’s at the office, during daily commutes, or while watching TV, extended sitting can lead to health issues. From increased chances of heart disease to poor posture, sitting for long periods is far from harmless. This article delves into why excessive sitting is a serious health concern. It also provides useful advice to tackle this modern-day problem.
Dangers
The dangers of extended sitting periods, particularly in relation to cardiovascular health, should not be overlooked. Long periods of inactivity obstruct proper blood circulation, leading to the accumulation of fatty acids in the arteries of the heart. Regardless of other contributing factors such as diet, age or exercise habits, people who sit for most of the day are at a higher risk of developing heart disease. These findings are compelling, urging people to rethink their daily habits involving prolonged sitting.
Extended sitting also significantly contributes to weight gain and the global obesity problem. When seated, your body’s metabolic rate drops drastically, leading to fewer calories being burned than when standing or moving. This metabolic decline leads to a slow but steady accumulation of body fat, especially in the abdominal area. There is worldwide rise in obesity and its associated health risks such as diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure. The link between a sedentary lifestyle and obesity is a pressing public health issue that needs immediate action.
The harmful effects of prolonged sitting go beyond physical health and also affect mental well-being. Sedentary behaviour has been associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety. Lack of physical activity can result in lower levels of endorphins, the ‘feel-good’ hormones. This can lead to feelings of sadness or depression. Furthermore, the absence of regular movement can heighten stress levels, making it harder for individuals to manage everyday pressures.
Taking Action
To combat the negative effects of prolonged sitting, incorporating more movement into your daily routine is an effective approach. Setting reminders to stand, stretch or walk around can break long periods of inactivity. Exercises such as squats or leg lifts can be performed even while at a desk, and combining these simple activities with short, brisk walks during breaks can drastically enhance circulation, metabolism and overall well-being.
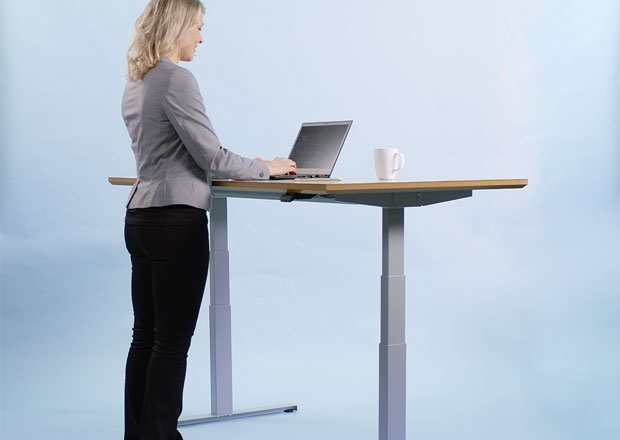
Investing in a standing desk such as an electric height adjustable standing desk can be a transformative decision to counteract the adverse effects of sitting for extended periods. These desks allow for a seamless transition between sitting and standing positions, enabling you to break the cycle of prolonged sitting without disrupting your workflow. Using a standing desk can significantly reduce your risk of weight gain, obesity and related complications like diabetes. Standing desks also improve mood and energy levels, potentially easing symptoms of depression and anxiety. They also promote better posture, reducing the risk of developing chronic back problems.
In this digital age, technology can be a useful tool to counteract the detrimental impacts of sitting for too long. There are various apps and smart devices designed to remind you to move, track your activity levels, and guide you through quick workouts that you can do at your desk or in a small space. Gadgets like smartwatches can monitor your heart rate, steps taken, and calories burned, providing valuable data that can motivate you to keep moving. These devices act as excellent accountability partners, encouraging you to meet your daily physical activity goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while prolonged sitting poses significant health risks, there are numerous ways to mitigate these risks. From incorporating more movement into your day to investing in the best sit stand desk, taking proactive measures can lead to improved physical and mental well-being.